Domain Name vs URL – If you’re building a website or diving into the world of online branding, you’ve probably encountered terms like domain name and URL. While they’re often used interchangeably, they refer to different aspects of your website’s address. Understanding the distinction is essential for creating and managing your online presence effectively.
Let’s break down the differences between a domain name and a URL, explore their purposes, and learn how they work together.
Table of Contents
What Is a Domain Name?
A domain name is the unique name that identifies a website on the internet. It’s essentially the address people type into their web browser to access your website.

Example:
- Domain Name:
example.com
Domain names are made up of two key parts:
- The Name: This is the identifier, such as “example” in
example.com. - The Extension: Also known as a Top-Level Domain (TLD), this includes
.com,.org,.net, or country-specific extensions like.ukor.ca.
Purpose of a Domain Name:
- Makes your website address easy to remember.
- Serves as your online identity, reflecting your brand or business name.
What Is a URL?
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the complete web address that directs users to a specific page, file, or resource on your website. It’s more detailed than a domain name and includes additional information like the protocol, subdomain, and path.

Example:
- URL:
https://www.example.com/blog/postor https://domainregistrationindia.co.in/blog/
Parts of a URL:
- Protocol: The communication method used by the browser (e.g.,
httporhttpsfor secure connections). - Subdomain: A prefix like
www,blog, orshopthat categorizes sections of a site (optional). - Domain Name: The main identifier (e.g.,
example.com). - Path: Specifies the exact page or file location (e.g.,
/blog/post).
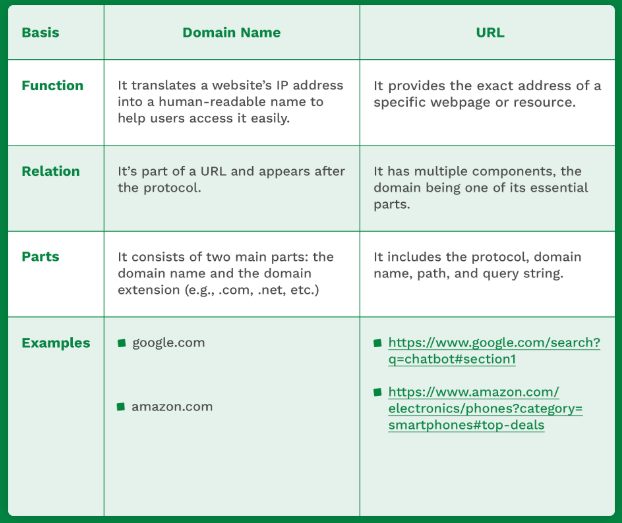
Key Differences Between Domain Name and URL (Domain Name vs URL)
| Feature | Domain Name | URL |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The unique name of a website. | The full web address that points to a specific page or resource. |
| Example | example.com | https://www.example.com/blog/post |
| Includes Protocol? | No | Yes (e.g., https://) |
| Includes Path? | No | Yes (e.g., /blog/post) |
| Function | Represents the website as a whole. | Directs users to a specific location or resource. |
Domain Name vs URL
Here are the key differences between a domain and a URL in a snapshot:
How Domain Names and URLs Work Together
Think of a domain name as the main address for your business, while a URL is the detailed map that guides visitors to the exact room or office. For example:
- Domain Name:
example.com
This is the general address of your website. - URL:
https://www.example.com/about-us
This guides visitors directly to the “About Us” page.
Without a domain name, a URL would rely on the website’s raw IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1), which is much harder to remember. Together, domain names and URLs make web navigation user-friendly.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
For Website Owners:
- Ease of Branding: Choose a memorable domain name for your business but understand how URLs impact navigation and SEO.
- SEO Benefits: URLs with clear paths and keywords can improve search engine rankings and user experience.
For Users:
- Security Awareness: Pay attention to URLs, especially the protocol (
https://), to ensure the site is secure. - Efficient Browsing: Recognize the structure of a URL to quickly locate the information you need.
Conclusion
While the terms domain name and URL are closely related, they serve distinct purposes. The domain name is the core identifier of your website, while the URL provides the complete address to a specific page or resource. Together, they form the backbone of internet navigation.
When creating your online presence, focus on selecting a strong, memorable domain name and structuring user-friendly URLs to enhance your website’s usability and credibility.
Domain Name vs URL Domain Name vs URL Domain Name vs URL Domain Name vs URL Domain Name vs URL Domain Name vs URL Domain Name vs URL


