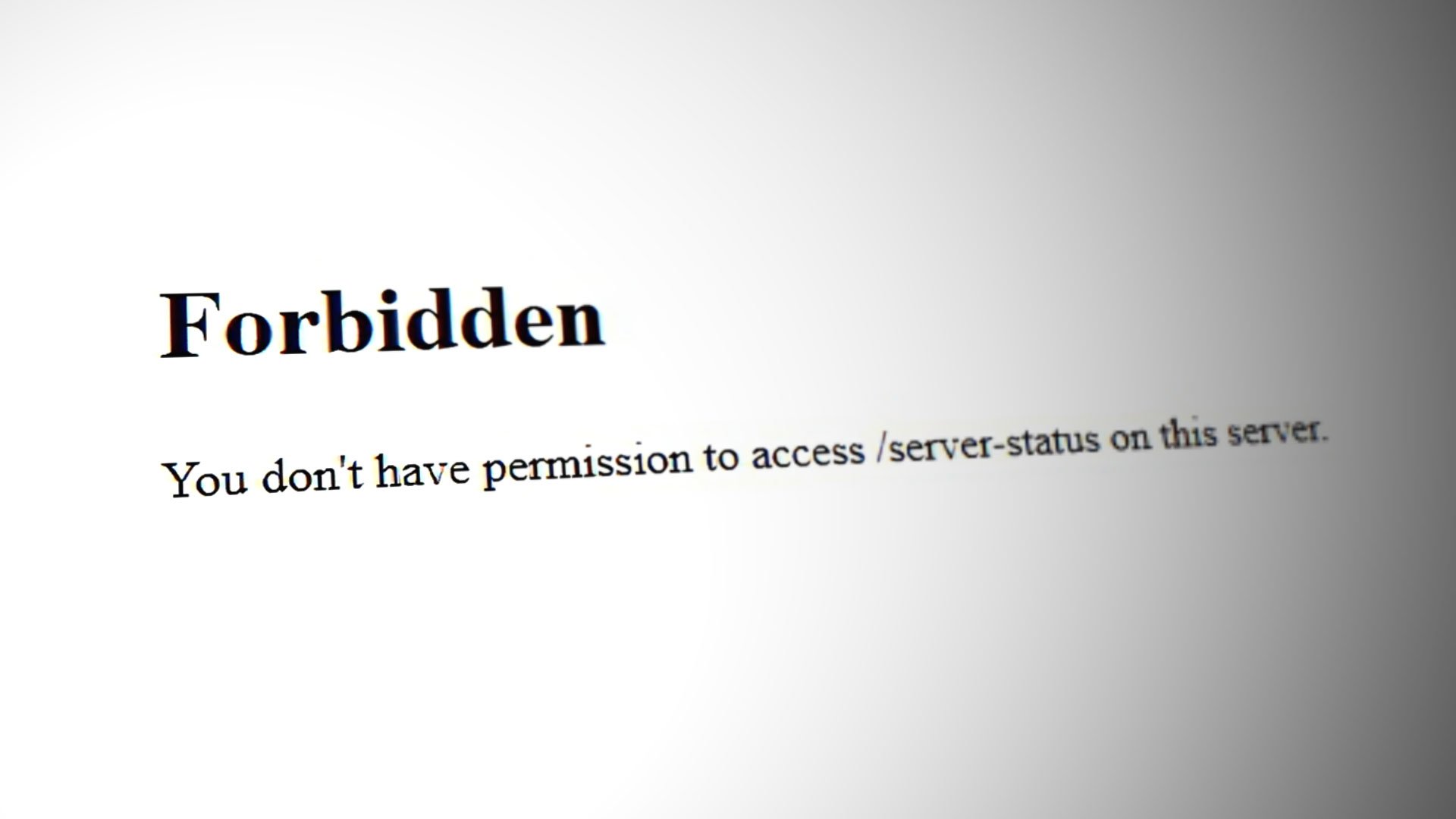
A Forbidden error, usually a 403 error, indicates that the server understands the request, but it refuses to authorize it
Table of Contents
Why Does the “You Don’t Have Permission to Access / On This Server” Error Occur?
The major causes of the “you don’t have permission to access / on this server” include a server-side issue with the website you are trying to access, interference from the browser’s cache and cookies, a website not being accessible in your geographical location, an interference from your ISP or merely using a proxy server on your Windows device.
To fix the “you don’t have permission to access / on this server” issue on your browser, you need to clear the browser’s cache and cookies, enable or disable a VPN, change the DNS, delete your browser history, or disable any proxy network you’re using. There may also be a need to reset or reinstall the browser if the major fixes do not work.
What Is the 403 Forbidden Error?
Also referred to as the 403 Forbidden error, Apache’s ‘Forbidden Error’ is an error that is displayed on a web page when you are attempting to access a website that’s restricted or forbidden.
It is a standardized HTTP status code indicating that the web server understands the request but is unable to authorize access due to permission issues.
It’s usually splashed on the browser as shown.
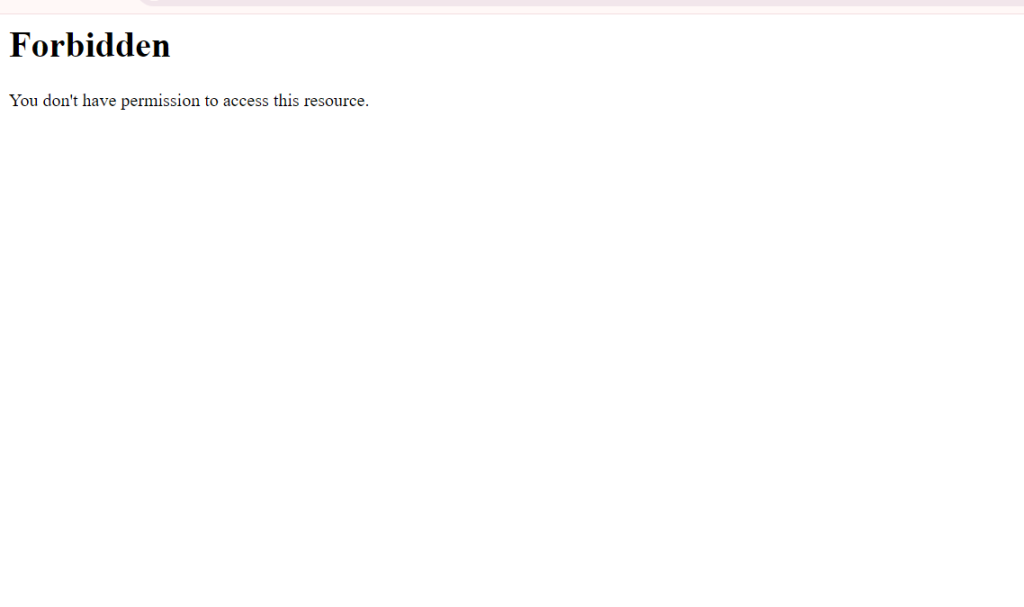
What Causes the Forbidden Error?
The ‘403 Forbidden Error‘ occurs due to the following main reasons:
1. Incorrect File / Directory Permissions
This error can be triggered due to incorrect file/folder permissions on the webroot directory. If the default file permissions are not adjusted to grant users access to the website files, then the chances of this error popping on a web browser are high.
2. Misconfiguration of the Apache Configuration Files
This error can also be attributed to a misconfiguration of one of the Apache configuration files. It could be an incorrect parameter that has been included or missing directives in the configuration file.
3. Misconfiguration of .htaccess File
Another frequent reason for encountering this HTTP response code is a damaged or improperly configured .htaccess file. When this occurs, the 403 Forbidden error typically surfaces after modifying the .htaccess file.
Typically, users can address this by either generating a new .htaccess file or rectifying its configurations.
4. Check File Ownership:
Ensure that the files and directories in your web server have the correct ownership. They should be owned by the user or account that the web server runs under.
5. Plugin/Theme Conflict:
If the error starts after installing a new plugin or theme, try disabling it to check if it’s causing the issue. Sometimes, conflicts between plugins or themes can trigger the 403 Forbidden error.
6. Clear Browser Cache:
Sometimes, the error might be cached in your browser. Clear your browser cache or try accessing the site from a different browser or device to see if the error persists.
7. Contact Hosting Support:
If none of the above steps resolve the issue, get in touch with your hosting provider’s support team. They can investigate further and identify the root cause of the 403 Forbidden error.
Fix the .htaccess File for Your WordPress Website
The .htaccess file serves as a distributed config file and tells the web server how to handle things like configuration changes per directory. Sometimes this file can get corrupted and may result in the “you don’t have permission to access / on this server” error.
Luckily, if that’s what is causing the 403 error on your server, you can easily fix this by creating a new .htaccess file. To create a new .htaccess file for your website, first, log in to your WordPress dashboard. Then, click on Settings > Permalinks.
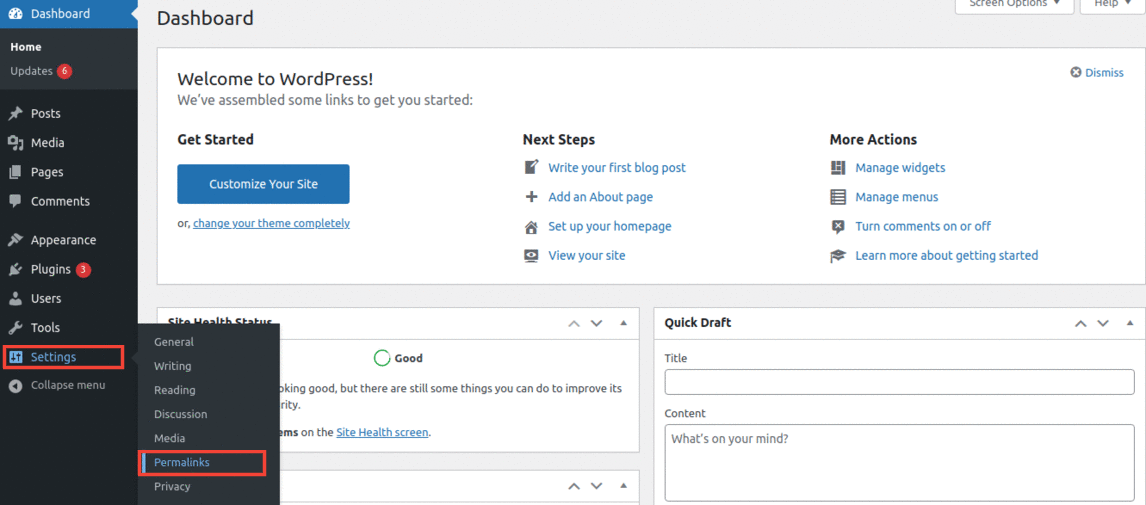
You don’t have to make any additional changes here. Just click on the Save Changes button and WordPress will generate a fresh .htaccess file for you.
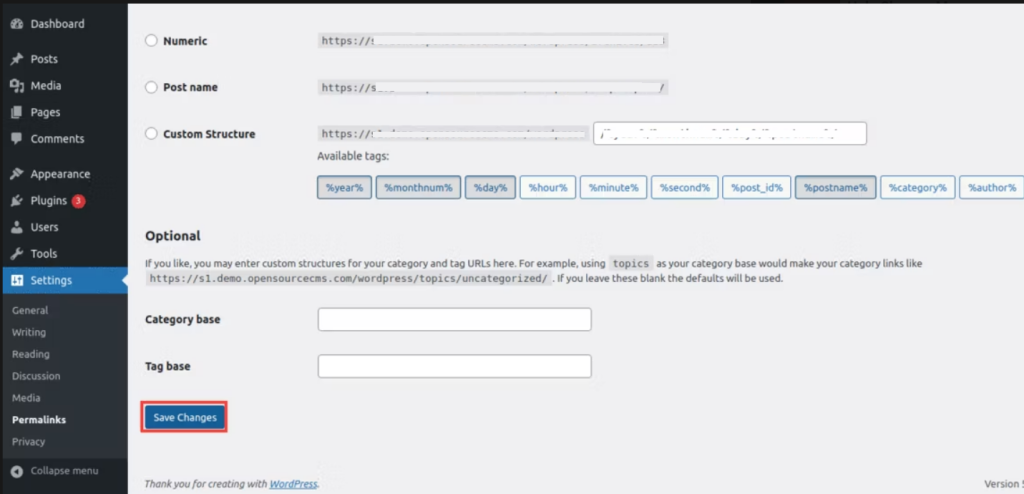
So anytime you see “you don’t have permission to access this resource” or “unable to read htaccess file, denying access to be safe” on Apache servers, try creating a new .htaccess file. This method usually works well for WordPress websites.