Table of Contents
History of Domains
Domain – Before the introduction of the Domain Name System (DNS) in 1983, users would access different addresses on computer networks through a host’s numerical address. Every computer on the network could then access files from the host by using said numerical addresses.
However, this process did not scale well and made public access difficult. Therefore, the DomainName System was introduced on ARPANET, a project that was essentially the foundation for the internet.
What is a domain name?
A domain-name is the identity of one or more IP addresses; for example, the domain name xyz.com points to the IP address “105.25.96.587”. Domain-names are invented as it is easy to remember a name rather than a long string of numbers. It would be easy to enter a domain-name in the search bar than a long sequence of numbers.

So, it is the web address of your website that people need to type in the browser URL bar to visit your website. In simple words, suppose your website is a house, then the domain-name is its address.
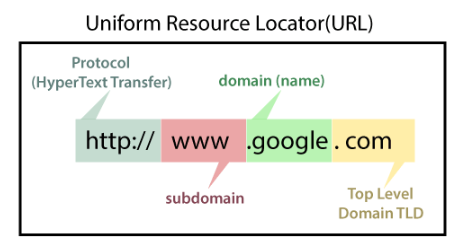
A domain-name cannot have more than sixty-three characters excluding .com, .net, .org, .edu, etc. The minimum length of a domain is one character excluding the extensions. It is entered in the URL after the protocol and subdomain as shown in the following example and the image:
E.g. https://www.google.com
https: (Protocol)
www.(Subdomain)
google.com (domain and domain suffix)
How Domain Name Works:
When the domain-name is entered in your web browser, a request is sent to the global network of servers that form the Domain Name System (DNS), which is like a phonebook of the internet.
The server then searches the name servers related to the domain and forwards the request to the name servers. The name servers are big computers, which are managed by hosting companies. The hosting company forwards the request to the webserver where your site is stored. The web server fetches the requested web page or information and forwards it to the browser.
The Domain Names System is managed by Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). It is a non-profit organization that creates and implements the policies for domain-names.
ICANN authorizes the companies called Domain-Name Registrars for selling domain names. It also allows them to make changes to domain-names registry on your behalf, and to sell domain names, manages their records, renewal, and transfer to other registrars. As a domain-name owner, you are required to renew your domain registration before it expires.


